Se habla español | We treat emergencies
1250 W. Lake St, Unit #20, Addison, IL 60101Se habla español | We treat emergencies
1250 W. Lake St, Unit #20, Addison, IL 60101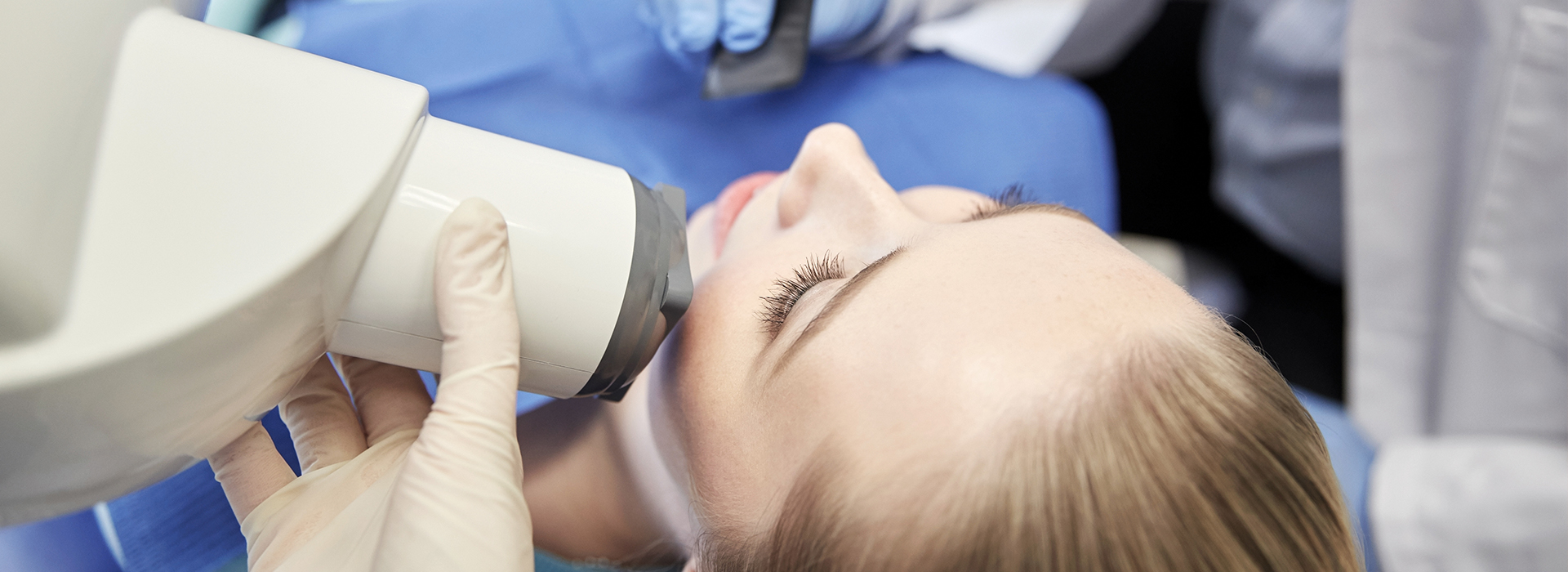
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with electronic sensors and software to capture dental images. Rather than waiting for film to develop, a sensor records the X‑ray and instantly transfers a clear, high‑resolution image to a computer. This transition from analog to digital has transformed how dentists evaluate tooth structure, bone, and restorations—making diagnostic images more accessible and easier to interpret in real time.
While the underlying physics of X‑ray generation remain the same, the workflow and capabilities change dramatically with digital systems. Images can be adjusted for contrast and zoomed in without retakes, which helps clinicians detect subtle issues. The result for patients is a faster visit and a more informed diagnostic process, with images available for immediate review alongside clinical findings.
Digital radiography also integrates with electronic health records and practice management software, so images become part of a patient’s long‑term record without the need for separate film storage. For practices that emphasize coordinated care and thorough documentation, that integration is a practical advantage that supports better continuity and follow‑up.
One of the most tangible benefits of digital radiography is speed. Images appear on the monitor moments after exposure, allowing clinicians to make quicker assessments and discuss findings with patients during the same appointment. This immediacy reduces uncertainty and shortens treatment planning cycles, which many patients appreciate when seeking answers during a single visit.
Image clarity and manipulability are additional patient advantages. Clinicians can enhance contrast, annotate areas of interest, and crop images to focus on specific anatomy without any loss of detail. Improved visualization helps identify cavities between teeth, cracks in restorations, and early signs of bone loss earlier than might be possible with lower‑quality film images.
From a safety perspective, modern digital sensors typically require less radiation than conventional film X‑rays to produce diagnostic images. That reduction aligns with best practice principles for minimizing exposure while still obtaining the information needed for accurate care. Combined with protective techniques and equipment, digital radiography contributes to a safer imaging experience for patients.
Digital radiography uses two main types of sensors: direct sensors that convert X‑ray energy into an electronic signal, and phosphor plate systems that capture an image which is then scanned. In either case, the resulting data are converted into a digital file that software can display, enhance, and store. This streamlined process eliminates chemical processing, reduces handling errors, and makes quality control simpler.
Specialized dental imaging software is central to the value of digital radiography. It manages file organization, patient labeling, and diagnostic tools such as measurement rulers, density histograms, and comparison views. Software also enables side‑by‑side comparisons of current and past images, helping clinicians track changes over time and evaluate the effects of treatment with confidence.
Because images are digital files, they can be shared securely with specialists or referring offices when coordination of care is required. Whether sending an image to an oral surgeon for implant planning or consulting with an endodontist about a root canal, the ability to transmit high‑quality images expedites decision making and helps ensure everyone involved has the same visual information.
Digital radiography is used across a wide range of dental procedures. Bitewing and periapical images remain essential for detecting cavities, evaluating the health of tooth roots, and examining bone height around teeth. Panoramic and specific intraoral views are frequently used for treatment planning in restorative, periodontal, and surgical care because they reveal anatomy that is not visible during a visual exam.
For restorative dentistry, precise images help determine the extent of decay and the relationship of existing restorations to surrounding tooth structure. In endodontics, high‑resolution digital images clarify canal anatomy and allow clinicians to monitor healing after treatment. For implant planning, radiographs complement other imaging—informing decisions about implant placement, angulation, and proximity to vital structures.
Digital imaging is also a useful monitoring tool in preventive care. Comparing images taken at different visits helps the dental team spot early changes in enamel, subtle bone loss, or developing pathology. Early detection supports less invasive treatment options and more predictable outcomes, which many patients find preferable to more extensive interventions later on.
Patient safety is a priority when imaging is performed. Digital systems often require lower exposure times, and modern sensors are more sensitive to X‑rays than older film, which contributes to dose reduction. Combined with appropriate shielding, correct technique, and adherence to recommended imaging intervals, digital radiography supports a conservative approach to radiation use.
Comfort and efficiency are two additional practical benefits. Sensors are thin and often less intrusive than older film holders, and the reduced need for retakes lowers appointment stress. Because images are accessible instantly, the clinician can explain findings using the image on screen, enhancing patient understanding and engagement in treatment decisions.
Environmental advantages should not be overlooked. Digital workflows eliminate the chemical developers and fixer solutions required for film processing and remove the need for film storage and disposal. This reduces hazardous waste and supports greener practice operations, an increasingly important consideration for both providers and patients.
In summary, digital radiography brings speed, diagnostic precision, and safer imaging into routine dental care. By combining modern sensors with advanced software, the practice achieves clearer images, streamlined workflows, and improved communication—benefits that directly support patient comfort and clinical outcomes. To learn more about how the office of Addison Dental Studio uses digital imaging in patient care, please contact us for additional information.
Digital radiography is a method of taking dental X-rays that uses electronic sensors and imaging software instead of traditional film. A sensor captures X-ray data and transfers a high-resolution image to a computer almost instantly, enabling immediate review and adjustment. This digital approach removes chemical processing and creates files that are easy to view, enhance, and archive.
Because images are available right away, clinicians can correlate radiographic findings with the clinical exam during the same visit. Digital files also support detailed manipulation such as contrast adjustment, zoom and measurement tools that help clarify anatomy. Taken together, these features make digital radiography an efficient and precise diagnostic tool in modern dental care.
Unlike film X-rays, digital radiography converts X-ray exposure directly into digital data, eliminating the need for chemical development and physical storage. Digital sensors capture images with improved sensitivity, which reduces the number of retakes and often lowers exposure time. The resulting files can be enhanced and reviewed on-screen, which is not possible with conventional film without scanning and processing.
The workflow is also more efficient because images integrate with electronic health records and practice management systems. Clinicians can compare current images with prior exams side by side and annotate areas of interest for documentation. This streamlining supports faster diagnosis and clearer communication between the dental team and patients.
Digital sensors are typically more sensitive than film, which generally allows clinicians to obtain diagnostic images with lower radiation exposure. When combined with appropriate shielding, proper technique and adherence to professional imaging guidelines, digital radiography supports a conservative approach to radiation use. These safety practices are standard in dental imaging to minimize exposure while ensuring diagnostic quality.
Safety also depends on selecting the right type of image for the clinical question and on individualized imaging intervals based on patient risk. Clinicians follow evidence-based protocols to determine when images are necessary, avoiding routine exposures that do not influence care. Patients with questions about radiation dose or protective measures should discuss concerns with their dental team for a clear, case-specific explanation.
Digital radiography primarily uses two sensor types: direct digital sensors that produce an electronic signal on exposure, and phosphor plate systems that capture an image which is subsequently scanned into a digital file. Intraoral sensors provide detailed periapical and bitewing views, while panoramic and cephalometric units offer broader overviews of dental and facial anatomy. Each system serves distinct clinical needs depending on the area being evaluated and the level of detail required.
Specialized software complements these sensors by managing files, patient labeling, measurements and comparison views. Advanced clinics may also use complementary technologies such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) for three-dimensional assessment when more complex anatomic information is needed. Choosing the correct sensor and software combination ensures images are optimized for the diagnostic task at hand.
Digital images can be enhanced with contrast and magnification tools that reveal subtle findings that might be missed on lower-quality film. Clinicians can annotate images, measure structures precisely and compare sequential exams to monitor changes over time. These capabilities improve detection of cavities, root fractures, periodontal bone loss and other pathologies that inform treatment decisions.
Instant availability of images also shortens the diagnostic loop, allowing clinicians to explain findings to patients during the same appointment and to make timely treatment recommendations. When coordinating care with specialists, high-quality digital files can be shared quickly to support collaborative planning. Overall, digital radiography contributes to more informed, predictable treatment strategies.
Yes. Bitewing and periapical digital images are routinely used to detect interproximal cavities, recurrent decay beneath restorations and changes in root structure. Enhanced image manipulation such as contrast adjustment and magnification helps identify early lesions that may be difficult to see clinically. Detecting issues at an earlier stage often allows for more conservative treatment options.
For bone level evaluation, intraoral and panoramic images provide views that reveal periodontal bone height and localized bone loss patterns. Serial radiographs taken over time are particularly valuable for monitoring disease progression or healing after treatment. The combination of clinical exam and targeted imaging delivers a more complete assessment of oral health.
Digital radiographs are stored as electronic files within the practice's imaging system and integrated electronic health records, which simplifies retrieval and long-term tracking. Modern dental practices use secure, HIPAA-compliant systems that include user authentication, encrypted data transmission and controlled access to protect patient information. These safeguards help ensure that images remain confidential and available only to authorized providers.
When collaboration with specialists or referring providers is necessary, images can be transmitted through secure channels or shared via encrypted portals to preserve privacy. This capability accelerates consults and treatment planning while maintaining compliance with privacy regulations. Proper file management also reduces errors associated with physical film handling and storage.
A digital X-ray appointment is typically quick and straightforward: the sensor or phosphor plate is placed in the mouth or positioned externally, an exposure is taken, and the resulting image appears on the clinician's monitor within seconds. Protective measures such as a lead apron or thyroid collar may be used according to clinical need and patient preference. The process generally causes little discomfort and is faster than conventional film imaging due to fewer retakes.
After the image is captured, the clinician will review it with the patient and explain any findings that relate to diagnosis or treatment planning. Enhanced views and annotated images help patients understand what the clinician observes and why certain recommendations are made. If additional or three-dimensional imaging is required, the clinician will explain the purpose and how it complements the digital radiographs.
Imaging intervals are individualized and based on a patient's oral health history, risk factors for disease, and current clinical findings rather than on the imaging technology itself. Professional guidelines recommend tailoring radiographic frequency to factors such as history of cavities, periodontal status and developmental considerations for younger patients. Clinicians use these criteria to balance diagnostic benefit with prudent radiation stewardship.
During routine visits, the dental team will review prior images and the clinical exam to determine whether new radiographs are necessary. Patients with new symptoms or clinical concerns may require targeted images regardless of the last routine radiograph. Open dialogue with your provider ensures imaging is ordered only when it will inform diagnosis or treatment.
Digital radiography is an integral part of comprehensive dental care because it provides high-quality images that support accurate diagnosis, conservative treatment planning and long-term monitoring. The technology enables clinicians to correlate radiographic findings with clinical exams and to document progress over time, which is essential for preventive, restorative and surgical care. Fast image availability also improves communication within the dental team and with consulting specialists.
At Addison Dental Studio, digital imaging is used alongside clinical evaluation and other diagnostic tools to ensure care decisions are well informed and properly documented. Secure electronic storage and image-sharing capabilities facilitate coordinated treatment when multiple providers are involved. Patients are encouraged to ask questions about any images so they can actively participate in decisions about their oral health.
Quick Links
Contact Us